Accelerating the Robot Dream
Empowering robot innovation, providing full-cycle development services, reducing costs, and accelerating the commercialization process.
Contact Us +


Henan Xspirebot
Xspirebot specializes in the design, production, and servicing of robot platform solutions.

Quality Control
A comprehensive quality control system that manages everything from raw materials to finished products.

Service & After sales
24-hour after-sales service. Please do not hesitate to contact us if you have any questions.

Download
XspireBot provide downloads of product catalogs, product solutions, and user manuals.

Key Member
Ten years of mass production experience and 32 patents in motion control.

Agricultural Industry
Agricultural robot chassis assists you in field operations such as sowing, spraying, and harvesting.

Manufacturing Industry
Industrial robot chassis assist you with tasks such as material handling, assembly, and quality inspection.

Transportation Industry
Autonomous transport robots that can deliver goods around the clock in urban and industrial environments.

Warehousing Industry
Unmanned transport robots enable full autonomy in cargo stacking & transfer within IoT logistics.

Inspection Industry
Autonomous 24/7 patrols at power facilities, industrial sites, data centers, and other locations.

Firefighting Industry
Autonomous fire detection & suppression in high-risk environments: high-rises, chemical plants, and data centers.

Robot Chassis
Xspirebot offers chassis for indoor and outdoor mobile robots suitable for different terrains.

Motors
Drive motor designed for mobile robot chassis, applied to mobile robot platform & agricultural robot chassis.

Controller/Drive
The controller can control the robot chassis's movement, positioning, obstacle avoidance, path planning, and other motion functions.

Sensor
Xspirebot offers advanced sensors for autonomous robot platforms: cameras, ultrasonic radar, LiDAR, IMU, & IINS.

Electric Motor Axle
Xspirebot adapts electric transaxle load, power output, & layout to meet customer needs.

Wired Components
Line control braking & steering enhance vehicle control efficiency & precision via electronic signals.

Energy
Solar panels & batteries offer flexible solutions, letting you choose components to suit your needs.

Company News
Xspirebot is committed to helping our customers reduce development costs, shorten the R&D cycle, and accelerate the mass production process through platformized and modularized architectural design and standardized production processes.

Exhibition News
Xspirebot is committed to helping our customers reduce development costs, shorten the R&D cycle, and accelerate the mass production process through platformized and modularized architectural design and standardized production processes.

Industry News
Xspirebot is committed to helping our customers reduce development costs, shorten the R&D cycle, and accelerate the mass production process through platformized and modularized architectural design and standardized production processes.
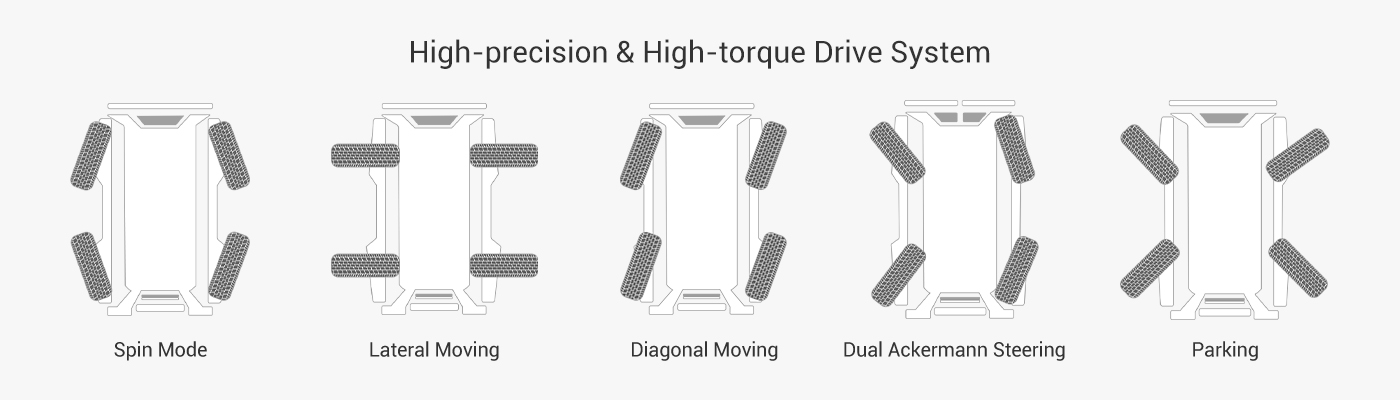
The 4Wd robot chassis is equipped with four independent drive wheels and four independent steering mechanisms, with each wheel controlled by an independent motor for forward, reverse, and steering movements, enabling omnidirectional mobility, zero turning radius, and multi-modal movement, including on-the-spot rotation, diagonal movement, and Ackermann steering, among other modes. It offers high maneuverability and off-road capability, making it suitable for complex terrains, indoor and outdoor inspections, security, agriculture, and logistics delivery scenarios; Compared to traditional four-wheel differential chassis, it eliminates the need for complex differentials, simplifying the structure and enhancing flexibility through independent steering and drive systems, while also supporting modular expansion.

The 4Wd robot chassis is equipped with four independent drive wheels and four independent steering mechanisms, with each wheel controlled by an independent motor for forward, reverse, and steering movements, enabling omnidirectional mobility, zero turning radius, and multi-modal movement, including on-the-spot rotation, diagonal movement, and Ackermann steering, among other modes. It offers high maneuverability and off-road capability, making it suitable for complex terrains, indoor and outdoor inspections, security, agriculture, and logistics delivery scenarios; Compared to traditional four-wheel differential chassis, it eliminates the need for complex differentials, simplifying the structure and enhancing flexibility through independent steering and drive systems, while also supporting modular expansion.

Parameter Table
| Applicable venues | Indoor and outdoor complex road conditions in multiple scenarios (asphalt roads, grass, gravel roads, epoxy flooring, obstacle crossing, climbing slopes) | |
| Model | 4 wheel robot smart car chassis kits | 4wd robot chassis |
| Dimensions | 680*550*440mm | 680*550*440mm |
| Load capacity | 50KG | 100KG |
| Speed (full load test) | 5.4km/h | 5.4km/h |
| Empty load range | 40km | 40km |
| Drive motor | 350W*4 servo motors | 350W*4 servo motors |
| External power supply | 12V/15A-24V/15A-48V/10A | 12V/15A-24V/15A-48V/10A |
| Braking method | Motor braking | Motor braking |
| Parking method | Motor parking + parking posture | Motor parking + parking posture |
| Water depth | 100mm | 100mm |
| Maximum climbing angle | No load 30°/full load 15° | No load 30°/full load 15° |
| Crossing width | Full load 120mm/No load 160mm | Full load 120mm/No load 160mm |
| Obstacle height | Full load 40mm/No load 60mm | Full load 40mm/No load 60mm |
| Communication method | CAN 2.0B | CAN 2.0B |
| Battery capacity | 48V/20Ah | 48V/20Ah |
| Charging time | 4–5 hours | 4-5 hours |
| Charging method | 48V/5A Manual charging/automatic charging | 48V/5A Manual charging/Automatic charging |
| Protection rating | IP33 | IP33 |

Structural Design and Modularization
The 4 wheel robot smart car chassis adopts a modular design, including the base frame, mounting slots, drive mechanism, and wheel assembly. The base frame is equipped with multiple through-type mounting slots, with side openings secured by sliders and protrusions, facilitating quick assembly and disassembly of the drive module. Compared to a four-wheel differential chassis, the four-wheel drive system eliminates complex components such as reducers, with motors driving directly, resulting in fewer parts, a more flexible internal space layout, and avoiding the issues of bulky volume and high failure rates caused by differential structures.
Suspension and Shock Absorption System: Equipped with independent suspension and shock absorption modules, including brackets, shock absorbers, buffers, and connecting rods. The shock absorbers are mounted on the brackets, with one end connected to the wheels via buffers for removable connection, and the other end connected via connecting rods for rotational movement, enabling adaptation to various terrains. The buffers can be rotatably connected to the shock absorbers to prevent vibrations from affecting the drive system. This enables the chassis to perform exceptionally well in off-road environments, absorbing impacts more effectively than the rigid structure of a four-wheel differential system, thereby reducing tire wear and position drift.
Drive and Steering System
Independent Drive and Steering: Each wheel is equipped with an independent drive motor (hub motor) and steering motor, with a total of 8 motors controlling movement. The drive module includes a housing, drive motor, and transmission assembly. Steering is achieved through linkage components for precise angle control, supporting a steering range of -90° to +90°. The wheels are built-in encoders and code disks, mounted on the mounting plate and integrated with the hub motor, reducing external components and simplifying wiring and debugging.
Unlike four-wheel differential steering, which relies on the speed difference between the left and right wheels, four-wheel steering and four-wheel drive use independent steering motors to avoid tire wear caused by sliding friction (especially on hard surfaces like concrete), enabling more flexible steering and achieving smooth, offset-free movement.
Efficient transmission and omnidirectional capability: The transmission assembly and linkage components drive the support frame to rotate, achieving omnidirectional movement without mileage deviation. Compared to the sliding friction steering of four-wheel differential systems, the four-wheel steering and four-wheel drive system offers higher transmission efficiency, longer tire life, and supports stable operation over extended periods.
Motion Mode
Multi-mode motion: Supports multiple modes, including dual Ackermann mode, lateral shift mode, on-the-spot rotation (zero turning radius), and “X”-shaped parking (no risk of rolling on long slopes). Four-wheel differential has only one differential mode, which is affected by ground friction, leading to position drift and high energy loss. In contrast, the independent control of four-wheel drive ensures high-precision positioning, making it suitable for narrow spaces and complex paths.
Performance Metrics and Load Capacity
Load and Off-Road Performance: Typical load capacity of 200 kg, with a climbing angle of up to 35°, enhanced shock absorption through independent suspension, strong maneuverability and off-road capability, suitable for various terrains such as steep slopes and indoor/outdoor transitions. It causes minimal tire wear and is suitable for long-term use on hard surfaces.

1. Indoor Environment
Narrow spaces and complex path operations: Suitable for small-sized, highly flexible applications, such as narrow passages or indoor inspections, supporting zero turning radius and diagonal movement modes for easy obstacle avoidance and operation in confined spaces. For example, delivery or cleaning tasks in office buildings, banks, or shopping malls.
Goods handling and logistics delivery: As an AGV (Automated Guided Vehicle) chassis, it is used for material transportation in indoor warehouses or factories, with strong load capacity (up to 200kg), suitable for service scenarios such as restaurants or shopping malls, enabling automated meal delivery or goods distribution.
Automatic parking and security patrols: In underground parking garages or indoor parking lots, it supports multi-sensor fusion (such as lidar) to achieve precise positioning and obstacle detection, suitable for automatic parking or security monitoring.
2. Outdoor Environment
Multi-terrain off-road and patrol: Equipped with independent suspension and shock absorption systems, with a climbing angle of up to 35°, suitable for outdoor complex terrains such as parks, industrial parks, or stations for inspection and monitoring, supporting indoor-outdoor cross-floor switching and all-terrain adaptability.
Large Public Area Maintenance: Used for security patrols or environmental monitoring in large-scale venues such as airports, train stations, or outdoor squares. Features long battery life and strong expandability, and can integrate cameras and sensors.
3. Indoor-outdoor integration scenarios
Mixed environment transportation and navigation: Supports SLAM (Simultaneous Localization and Mapping) autonomous positioning, suitable for indoor-outdoor transition areas such as industrial parks or parking garages, enabling seamless switching, such as the transfer of goods from warehouses to outdoor parks by logistics AGVs.
Service robot smart chassis applications: Used in semi-open spaces such as hospitals, hotels, or exhibition halls for guidance, delivery, or interactive services, combined with human-machine interaction-oriented designs to enhance the user experience.
4. Industrial and agricultural scenarios
Industrial transportation and special vehicles: Heavy load, high stability, suitable for heavy object transportation in factory production lines or industrial parks, supports multi-sensor fusion decision-making planning, and adapts to high-intensity operations.
Agricultural greenhouse operations: The 4 wheel robot smart car chassis width can be adjusted to suit different track gauges, suitable for spraying, picking, or monitoring in greenhouses, and supports stable operation on muddy or uneven terrain with four-wheel independent drive.

Related Accessories
Accelerating the Robot Dream
Empowering robot innovation, providing full-cycle development services, reducing costs, and accelerating the commercialization process.
Contact Us +