Accelerating the Robot Dream
Empowering robot innovation, providing full-cycle development services, reducing costs, and accelerating the commercialization process.
Contact Us +


Henan Xspirebot
Xspirebot specializes in the design, production, and servicing of robot platform solutions.

Quality Control
A comprehensive quality control system that manages everything from raw materials to finished products.

Service & After sales
24-hour after-sales service. Please do not hesitate to contact us if you have any questions.

Download
XspireBot provide downloads of product catalogs, product solutions, and user manuals.

Key Member
Ten years of mass production experience and 32 patents in motion control.

Agricultural Industry
Agricultural robot chassis assists you in field operations such as sowing, spraying, and harvesting.

Manufacturing Industry
Industrial robot chassis assist you with tasks such as material handling, assembly, and quality inspection.

Transportation Industry
Autonomous transport robots that can deliver goods around the clock in urban and industrial environments.

Warehousing Industry
Unmanned transport robots enable full autonomy in cargo stacking & transfer within IoT logistics.

Inspection Industry
Autonomous 24/7 patrols at power facilities, industrial sites, data centers, and other locations.

Firefighting Industry
Autonomous fire detection & suppression in high-risk environments: high-rises, chemical plants, and data centers.

Robot Chassis
Xspirebot offers chassis for indoor and outdoor mobile robots suitable for different terrains.

Motors
Drive motor designed for mobile robot chassis, applied to mobile robot platform & agricultural robot chassis.

Controller/Drive
The controller can control the robot chassis's movement, positioning, obstacle avoidance, path planning, and other motion functions.

Sensor
Xspirebot offers advanced sensors for autonomous robot platforms: cameras, ultrasonic radar, LiDAR, IMU, & IINS.

Electric Motor Axle
Xspirebot adapts electric transaxle load, power output, & layout to meet customer needs.

Wired Components
Line control braking & steering enhance vehicle control efficiency & precision via electronic signals.

Energy
Solar panels & batteries offer flexible solutions, letting you choose components to suit your needs.

Company News
Xspirebot is committed to helping our customers reduce development costs, shorten the R&D cycle, and accelerate the mass production process through platformized and modularized architectural design and standardized production processes.

Exhibition News
Xspirebot is committed to helping our customers reduce development costs, shorten the R&D cycle, and accelerate the mass production process through platformized and modularized architectural design and standardized production processes.

Industry News
Xspirebot is committed to helping our customers reduce development costs, shorten the R&D cycle, and accelerate the mass production process through platformized and modularized architectural design and standardized production processes.
Robot chassis navigation methods are core technologies enabling autonomous mobility for mobile robots (such as AGVs, service robots, or autonomous robots), primarily involving positioning, path planning, and obstacle avoidance. Based on current technological advancements, common navigation methods include laser SLAM navigation, landmark navigation (including magnetic navigation and QR code navigation), visual navigation, and inertial navigation. These methods exhibit significant differences in principles, accuracy, environmental adaptability, cost, and applicable scenarios. Do you know how to select the appropriate navigation method?
Laser SLAM Navigation
Laser SLAM navigation is a technology enabling robotic chassis to simultaneously perform self-localization and environmental mapping in unknown environments. It features autonomous mapping and autonomous navigation capabilities. Autonomous mapping refers to a mobile robot vehicle establishing a corresponding map after traversing any unfamiliar scene just once. Autonomous navigation enables free navigation, automatic path planning, and self-driving without any auxiliary positioning infrastructure. Its core lies in the laser SLAM algorithm, which processes LiDAR scan data to achieve real-time positioning and map updates during robot operation.
Principle: The robot emits laser beams via LiDAR, calculates distances by receiving reflected signals, and integrates IMU (inertial measurement unit) data to execute SLAM algorithms. This constructs centimeter-level maps, enabling autonomous positioning and path planning.
Applicable Scenarios: Warehouses, hospitals, and home service robots.

Waypoint Navigation (including magnetic navigation and QR code navigation)
Magnetic strip navigation is an automated guidance technology that employs magnetic strips pre-installed on the floor. Utilizing magnetic sensors on AGVs (Automated Guided Vehicles) or mobile robots to detect the magnetic field signals generated by these strips, it enables path recognition, positioning, and directional control.
Magnetic strips serve as fixed path markers that, once laid on the ground, remain virtually unaffected by environmental factors. They do not fail due to changes in light, dust accumulation, or object obstruction. They are highly suitable for scenarios with complex yet relatively fixed pathways, such as logistics warehouses, automotive manufacturing, or other industrial production lines.
The working principle of magnetic strip navigation primarily involves three stages: magnetic field signal generation, magnetic field detection, and path tracking.
Magnetic strips are typically made of ferromagnetic materials capable of continuously generating stable magnetic field signals.
Magnetic sensors mounted beneath the AGV body detect real-time changes in the magnetic field's intensity and direction.
By comparing signal differences between left and right sensors, the system calculates the AGV's deviation relative to the magnetic strip's centerline and adjusts the drive wheels' steering to achieve automatic path tracking.
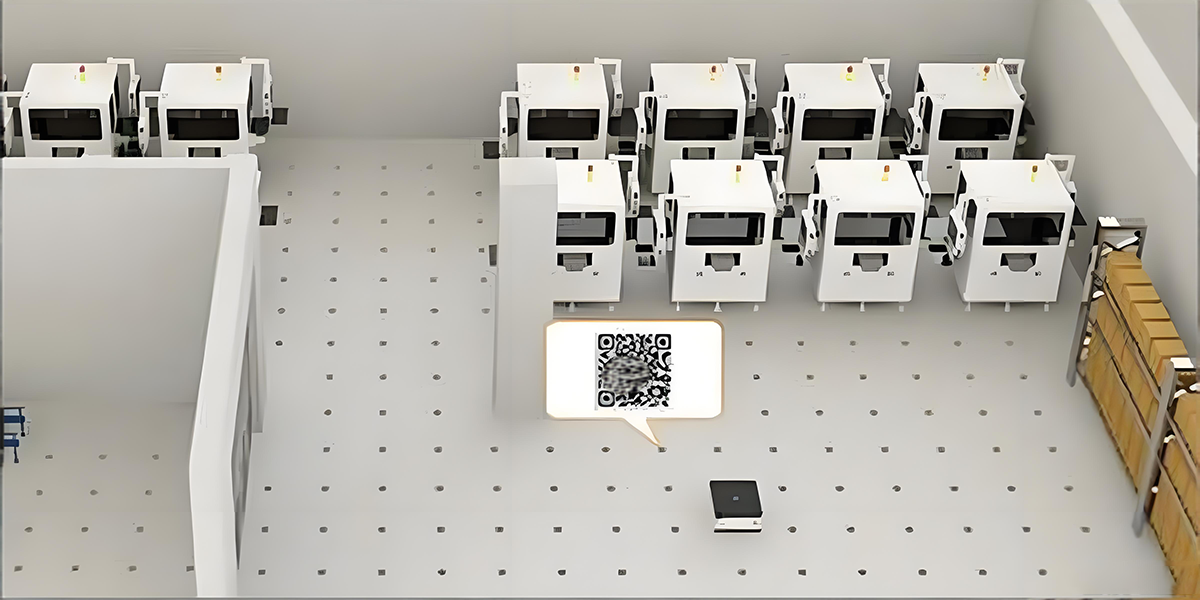
QR Code Navigation achieves precise positioning and path planning through the coordinated operation of ground-based QR codes and onboard visual systems. The core principles are as follows:
QR Code Functions
Positioning: QR codes contain coordinate identifiers (e.g., “A15”). AGVs determine their location by recognizing these codes.
Direction Recognition: QR code patterns incorporate orientation angles to help AGVs determine rotation angles.
Action Triggering: Certain QR codes can be programmed with action commands (e.g., “decelerate,” “turn”).
Map Calibration: Real-time correction of positioning deviations caused by wheel slippage or other factors.
Workflow
QR Code Scanning: An onboard industrial camera scans ground QR codes at a frequency of 20–30 milliseconds.
Image Processing: The vision system performs noise reduction, binarization, and edge detection.
Decoding: Algorithms identify the encoded content within the QR code.
Positioning Fusion: Integrates the QR code location with the vehicle's own posture to derive precise coordinates.
Behavior Response: The system calculates the next path based on position and task instructions.
Application Scenarios
Suitable for industrial and logistics sectors, such as material handling and conveying. It excels particularly in scenarios requiring millimeter-level high-precision positioning.
Selecting a navigation method requires balancing factors based on the robot's application scenario (e.g., indoor/outdoor, fixed/dynamic paths). If you require detailed examples for a specific method, please provide more details, and feel free to contact us anytime.
Accelerating the Robot Dream
Empowering robot innovation, providing full-cycle development services, reducing costs, and accelerating the commercialization process.
Contact Us +