Accelerating the Robot Dream
Empowering robot innovation, providing full-cycle development services, reducing costs, and accelerating the commercialization process.
Contact Us +


Henan Xspirebot
Xspirebot specializes in the design, production, and servicing of robot platform solutions.

Quality Control
A comprehensive quality control system that manages everything from raw materials to finished products.

Service & After sales
24-hour after-sales service. Please do not hesitate to contact us if you have any questions.

Download
XspireBot provide downloads of product catalogs, product solutions, and user manuals.

Key Member
Ten years of mass production experience and 32 patents in motion control.

Agricultural Industry
Agricultural robot chassis assists you in field operations such as sowing, spraying, and harvesting.

Manufacturing Industry
Industrial robot chassis assist you with tasks such as material handling, assembly, and quality inspection.

Transportation Industry
Autonomous transport robots that can deliver goods around the clock in urban and industrial environments.
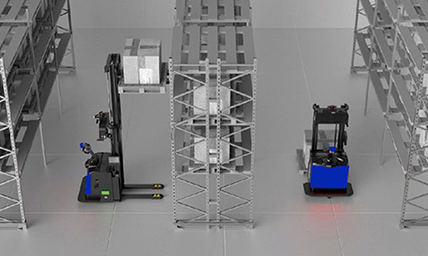
Warehousing Industry
Unmanned transport robots enable full autonomy in cargo stacking & transfer within IoT logistics.

Inspection Industry
Autonomous 24/7 patrols at power facilities, industrial sites, data centers, and other locations.

Firefighting Industry
Autonomous fire detection & suppression in high-risk environments: high-rises, chemical plants, and data centers.

Robot Chassis
Xspirebot offers chassis for indoor and outdoor mobile robots suitable for different terrains.

Motors
Drive motor designed for mobile robot chassis, applied to mobile robot platform & agricultural robot chassis.

Controller/Drive
The controller can control the robot chassis's movement, positioning, obstacle avoidance, path planning, and other motion functions.

Sensor
Xspirebot offers advanced sensors for autonomous robot platforms: cameras, ultrasonic radar, LiDAR, IMU, & IINS.

Electric Motor Axle
Xspirebot adapts electric transaxle load, power output, & layout to meet customer needs.

Wired Components
Line control braking & steering enhance vehicle control efficiency & precision via electronic signals.

Energy
Solar panels & batteries offer flexible solutions, letting you choose components to suit your needs.

Company News
Xspirebot is committed to helping our customers reduce development costs, shorten the R&D cycle, and accelerate the mass production process through platformized and modularized architectural design and standardized production processes.

Exhibition News
Xspirebot is committed to helping our customers reduce development costs, shorten the R&D cycle, and accelerate the mass production process through platformized and modularized architectural design and standardized production processes.

Industry News
Xspirebot is committed to helping our customers reduce development costs, shorten the R&D cycle, and accelerate the mass production process through platformized and modularized architectural design and standardized production processes.
Steering Drive Motor
Steering drive motor is a modular actuator that integrates both steering and driving functions, specifically designed for mobile robot chassis. It is commonly used in Mobile Robot Bases, Automated Guided Vehicle Chassis, and Agricultural Robot Chassis.
Its core components include a servo motor, reducer, encoder, and steering mechanism, enabling precise angle control and reliable power output. This type of motor supports various motion modes, including differential steering, Ackermann steering, and omnidirectional movement (e.g., using Mecanum wheels).
Advantage
Modular Design: Featuring standardized mechanical interfaces (such as flanges and keyways) and electrical connectors, the system is compatible with mainstream robot chassis architectures, supporting quick replacement and scalability.
Multi-Protocol Compatibility: The communication interface supports PWM analog control, CANopen motion control protocol (compliant with CiA402 standard), and EtherCAT high-speed bus, meeting the requirements of various automation systems.
Environmental Robustness: With an IP54 protection rating and wide temperature range design (-20°C to +60°C), it is suitable for industrial environments with dust, humidity, and large temperature variations—such as logistics warehouses, factory production lines, and outdoor inspection applications.
Safety Mechanisms: Built-in protections include overcurrent protection, overtemperature protection, and mechanical limit switches, preventing damage to the motor or load under abnormal operating conditions.
Torque Requirements: Torque is influenced by factors such as load weight, driving surface, tire material, and vehicle speed. For example, a fully loaded mobile robot chassis requires significantly more torque to initiate turning from a stationary position than when already in motion.
Sensor Types
Relative Position Feedback
Requires an initialization sequence (homing sequence), is cost-effective, and is suitable for simple systems.
Absolute Position Sensing
Uses Hall effect sensors or multi-turn absolute position sensors, does not require initialization, is economical and reliable, and is commonly used in industrial robots.
Safety
In environments where humans coexist, steering wheel systems must meet strict safety standards, such as redundant design and fault detection, to ensure safety.
Braking System
In steering wheel motors, brakes are primarily used for parking braking after stopping to prevent vehicle or equipment movement, ensuring stability and safety. This is typically achieved by applying a torque opposite to the motor's rotation direction, causing the motor to decelerate rapidly and stop rotating.
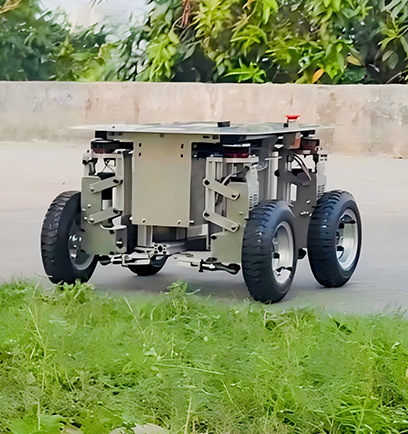
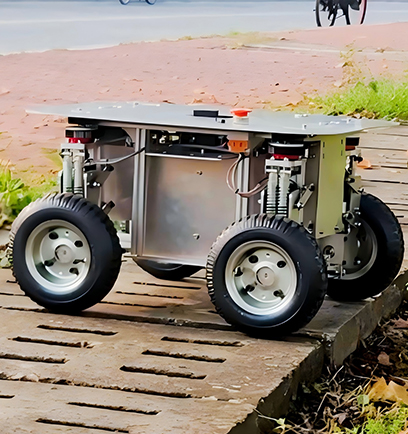
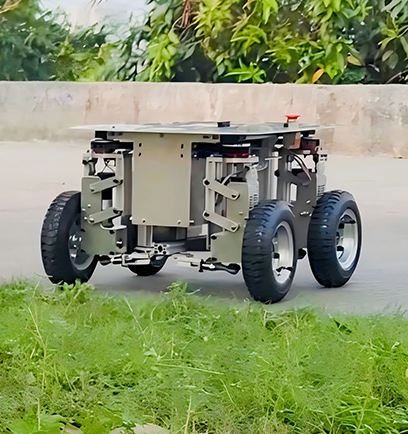
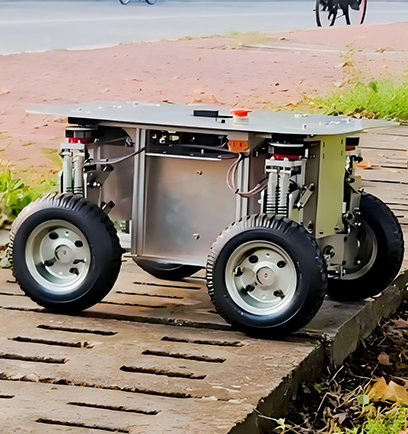




Product Classification
Accelerating the Robot Dream
Empowering robot innovation, providing full-cycle development services, reducing costs, and accelerating the commercialization process.
Contact Us +