Accelerating the Robot Dream
Empowering robot innovation, providing full-cycle development services, reducing costs, and accelerating the commercialization process.
Contact Us +


Henan Xspirebot
Xspirebot specializes in the design, production, and servicing of robot platform solutions.

Quality Control
A comprehensive quality control system that manages everything from raw materials to finished products.

Service & After sales
24-hour after-sales service. Please do not hesitate to contact us if you have any questions.

Download
XspireBot provide downloads of product catalogs, product solutions, and user manuals.

Key Member
Ten years of mass production experience and 32 patents in motion control.

Agricultural Industry
Agricultural robot chassis assists you in field operations such as sowing, spraying, and harvesting.

Manufacturing Industry
Industrial robot chassis assist you with tasks such as material handling, assembly, and quality inspection.

Transportation Industry
Autonomous transport robots that can deliver goods around the clock in urban and industrial environments.
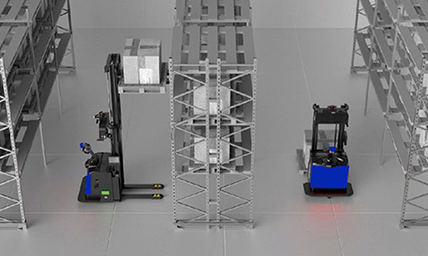
Warehousing Industry
Unmanned transport robots enable full autonomy in cargo stacking & transfer within IoT logistics.

Inspection Industry
Autonomous 24/7 patrols at power facilities, industrial sites, data centers, and other locations.

Firefighting Industry
Autonomous fire detection & suppression in high-risk environments: high-rises, chemical plants, and data centers.

Robot Chassis
Xspirebot offers chassis for indoor and outdoor mobile robots suitable for different terrains.

Motors
Drive motor designed for mobile robot chassis, applied to mobile robot platform & agricultural robot chassis.

Controller/Drive
The controller can control the robot chassis's movement, positioning, obstacle avoidance, path planning, and other motion functions.

Sensor
Xspirebot offers advanced sensors for autonomous robot platforms: cameras, ultrasonic radar, LiDAR, IMU, & IINS.

Electric Motor Axle
Xspirebot adapts electric transaxle load, power output, & layout to meet customer needs.

Wired Components
Line control braking & steering enhance vehicle control efficiency & precision via electronic signals.

Energy
Solar panels & batteries offer flexible solutions, letting you choose components to suit your needs.

Company News
Xspirebot is committed to helping our customers reduce development costs, shorten the R&D cycle, and accelerate the mass production process through platformized and modularized architectural design and standardized production processes.

Exhibition News
Xspirebot is committed to helping our customers reduce development costs, shorten the R&D cycle, and accelerate the mass production process through platformized and modularized architectural design and standardized production processes.

Industry News
Xspirebot is committed to helping our customers reduce development costs, shorten the R&D cycle, and accelerate the mass production process through platformized and modularized architectural design and standardized production processes.
Steering-by-Wire
Steering-by-Wire (SBW) technology is an advanced robot chassis steering technology that uses algorithms to eliminate the mechanical connection between the control handle and the moving mechanism, achieving steering control through electrical signals. This technology makes control safer, more flexible, and more precise, while also providing a technical foundation for advanced autonomous driving or autonomous mobility.
On robotic chassis, the application of SBW technology enables more flexible steering and movement, enhancing the robot's maneuverability and adaptability. Additionally, eliminating mechanical connections reduces the weight and cost of the robotic chassis, thereby improving its overall performance.
Operational Advantages
The operational advantages of wire-controlled steering technology in robots are mainly reflected in the following aspects:
Precise Control
Electric signal-controlled steering is more precise and can achieve small steering adjustments, improving the maneuverability of robots.
Easy to Program
Wire-controlled steering systems are easier to integrate with robot control systems to achieve automated steering control.
Fault Detection
Wire-controlled steering systems typically feature fault detection capabilities, enabling real-time monitoring of system operational status and prompt alerts or emergency measures when faults occur.
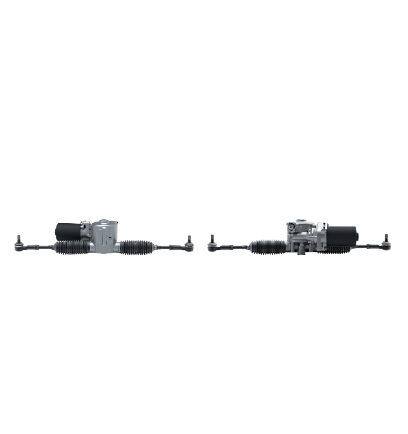
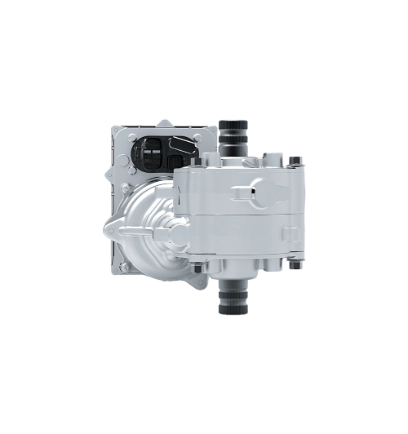
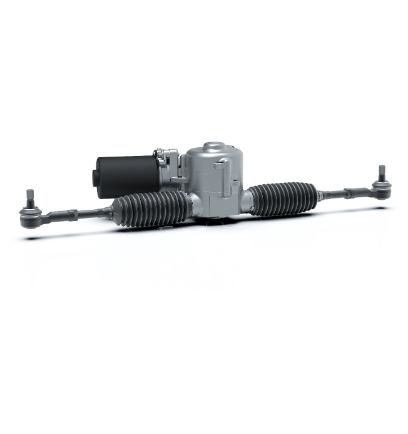



Advantages
Wireless steering technology, in simple terms, refers to controlling steering through electrical signals rather than traditional mechanical connections. On the robot chassis, the advantages of this technology are primarily reflected in the following aspects:
Enhanced Flexibility: SBW enables the robot chassis to perform more flexible steering maneuvers, adapting to various complex scenarios.
Weight Reduction: By eliminating mechanical connections, the overall weight of the robot chassis is reduced, which significantly aids in improving the robot's mobility and efficiency.
Safety Redundancy: Dual controller + multi-power backup design automatically switches in case of failure, ensuring the safety of emergency braking or evasive maneuvers.
Intelligent Collaboration: Seamless integration with navigation systems (such as lidar, SLAM) enables autonomous path planning and real-time adjustments, improving automation efficiency.
Cost Reduction: The maintenance cost of the steer-by-wire system is relatively low, as it reduces wear and replacement needs for mechanical components.
Scene Adaptability: Suitable for industrial AGVs, robot chassis, special-purpose robot chassis, and other scenarios, supporting stable steering in extreme environments such as high/low temperatures, underwater, and steep slopes.
Safety Boundaries
On a robot chassis equipped with line control steering technology, the setting of safety boundaries is critical. The following are some principles for setting safety boundaries:
Redundant Design: To ensure the reliability of the steering system, a redundant design is adopted. That is, when the main steering system fails, the backup system can immediately take over and continue to perform the steering task.
Fault Detection and Handling: The steer-by-wire system is equipped with fault detection and handling mechanisms that monitor the system's operational status in real time and take appropriate measures when faults occur.
Speed and Travel Limits: Based on the specific application scenarios and performance characteristics of the robotic chassis, reasonable speed and travel limit parameters are set to prevent safety incidents caused by loss of steering control.
Personnel Training and Monitoring: Personnel operating the robot chassis should undergo professional training and assessment to ensure they are familiar with the robot's operating procedures and safety standards. Additionally, personnel should monitor the robot chassis in real time during operation to ensure safety.
Performance parameters
| Serial number | Project Name | Unit | Parameter |
| 1 | Motor Rated Voltage | V | DC 12V |
| 2 | Motor Rated Power | W | 400 |
| 3 | Motor Rated Torque | Nm | 3.4 |
| 4 | Input Angle Range | ° | ±500 |
| 5 | Maximum Output Current | A | 36 |
| 6 | Rack Travel | mm | 123 |
| 7 | Rack Lateral Thrust | N | 4000 |
| 8 | Single-axis Load | Kg | 750 |
| 9 | Controller Operating Voltage | V | DC 12V |
| 10 | Rotation Direction | two-way | |
| 11 | Assembly Operating Temperature Range | °C | -40~+105 |
| 12 | Insulation Withstand Voltage | V | 240 |
| 13 | Insulation Temperature | °C | 500 |
| 14 | Waterproof Rating | IP67 (excluding connectors) |
Why choose a steer-by-wire system?
Steer-by-wire System
Eliminates mechanical connections. Steering signals are transmitted via electrical signals to the ECU control unit, which then drives the wheels to turn using an electric motor. A backup mechanical connection is only activated in the event of a failure.
Steer-by-wire systems typically offer higher steering precision and response speed.
Traditional Steering System
Relies on rigid mechanical connections between the steering wheel and wheels (such as the steering shaft and gears) to achieve steering through physical transmission.
For example, electric power steering (EPS) retains the mechanical structure but adds motor assistance.

Product Classification
Accelerating the Robot Dream
Empowering robot innovation, providing full-cycle development services, reducing costs, and accelerating the commercialization process.
Contact Us +