Accelerating the Robot Dream
Empowering robot innovation, providing full-cycle development services, reducing costs, and accelerating the commercialization process.
Contact Us +


Henan Xspirebot
Xspirebot specializes in the design, production, and servicing of robot platform solutions.

Quality Control
A comprehensive quality control system that manages everything from raw materials to finished products.

Service & After sales
24-hour after-sales service. Please do not hesitate to contact us if you have any questions.

Download
XspireBot provide downloads of product catalogs, product solutions, and user manuals.

Key Member
Ten years of mass production experience and 32 patents in motion control.

Agricultural Industry
Agricultural robot chassis assists you in field operations such as sowing, spraying, and harvesting.

Manufacturing Industry
Industrial robot chassis assist you with tasks such as material handling, assembly, and quality inspection.

Transportation Industry
Autonomous transport robots that can deliver goods around the clock in urban and industrial environments.
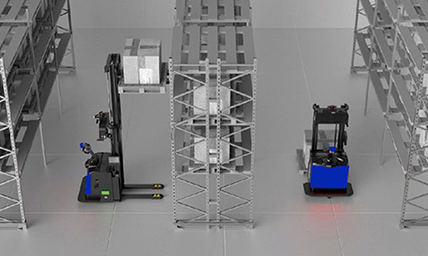
Warehousing Industry
Unmanned transport robots enable full autonomy in cargo stacking & transfer within IoT logistics.

Inspection Industry
Autonomous 24/7 patrols at power facilities, industrial sites, data centers, and other locations.

Firefighting Industry
Autonomous fire detection & suppression in high-risk environments: high-rises, chemical plants, and data centers.

Robot Chassis
Xspirebot offers chassis for indoor and outdoor mobile robots suitable for different terrains.

Motors
Drive motor designed for mobile robot chassis, applied to mobile robot platform & agricultural robot chassis.

Controller/Drive
The controller can control the robot chassis's movement, positioning, obstacle avoidance, path planning, and other motion functions.

Sensor
Xspirebot offers advanced sensors for autonomous robot platforms: cameras, ultrasonic radar, LiDAR, IMU, & IINS.

Electric Motor Axle
Xspirebot adapts electric transaxle load, power output, & layout to meet customer needs.

Wired Components
Line control braking & steering enhance vehicle control efficiency & precision via electronic signals.

Energy
Solar panels & batteries offer flexible solutions, letting you choose components to suit your needs.

Company News
Xspirebot is committed to helping our customers reduce development costs, shorten the R&D cycle, and accelerate the mass production process through platformized and modularized architectural design and standardized production processes.

Exhibition News
Xspirebot is committed to helping our customers reduce development costs, shorten the R&D cycle, and accelerate the mass production process through platformized and modularized architectural design and standardized production processes.

Industry News
Xspirebot is committed to helping our customers reduce development costs, shorten the R&D cycle, and accelerate the mass production process through platformized and modularized architectural design and standardized production processes.
LiDAR
LiDAR is a core sensor that enables robot chassis to achieve autonomy and intelligence. With its high-precision 3D environmental perception capability, it supports navigation, obstacle avoidance, and safe operation. By emitting laser pulses and measuring their return time, LiDAR generates accurate 3D maps that help robots identify distant targets and navigate complex scenes, driving automation and standardization across industries such as logistics, manufacturing, and agriculture.
Core Features
In robotic systems, lidar is typically installed on the top, front, or sides of the chassis, performing core functions such as environmental modeling, positioning and navigation, and obstacle avoidance planning.
Environmental Perception: Creates real-time 3D maps to support robot localization and path planning. For example, in automated warehouses, LiDAR helps cargo robots generate 3D models of shelves.
Centimeter-Level Positioning: Using Simultaneous Localization and Mapping (SLAM) technology, LiDAR builds dynamic maps in real time and corrects the robot's position, enabling centimeter-level accuracy even in complex environments.
Object Detection and Tracking: Detects the distance, shape, and movement trajectory of surrounding obstacles, providing real-time feedback for chassis motion control. This includes adjusting travel routes, avoiding dynamic obstacles, or adapting to terrain changes.
Examples:In delivery robots, LiDAR enables long-range trajectory prediction through multi-angle scanning. In industrial AGVs, it works with multiple sensors to achieve high-precision collision prevention. In service robots, it supports safe interaction in crowded environments.
Safe Operation: Provides millimeter-level distance measurement in complex scenarios such as city streets or tunnels, making it ideal for long-range and complex environments, greatly reducing the risk of collisions.
Advantages of LiDAR
Compared with ordinary microwave radar, laser radar uses laser beams and operates at a much higher frequency than microwaves, which brings many advantages, mainly:
1. High Resolution
LiDAR can achieve extremely high angular, distance, and velocity resolution. It can distinguish between two targets 0.3 meters apart at a distance of 3 kilometers and track multiple targets simultaneously. Distance resolution can reach 0.1 meters, and velocity resolution can reach within 10 meters per second, enabling precise identification of lane lines, curbs, and small obstacles (such as tire debris).
2. Strong Anti-Interference Capability
There are few signal sources in nature that can interfere with lidar, so lidar has strong resistance to active interference.
3. Excellent Low-Altitude Detection Performance
Microwave radar has blind spots (areas that cannot be detected) at low altitudes due to the influence of various ground echoes. For laser radar, only illuminated targets produce reflections, and there is no influence from ground echoes.
4. Compact Size and Lightweight
The aperture of a laser radar transmitter is typically only a few centimeters in diameter, and the entire system can weigh as little as a few dozen kilograms, making it easy to set up and dismantle. Additionally, the structure of laser radar is relatively simple, making it easy to maintain, operate, and cost-effective.
5. Penetration Capability
Lasers with a wavelength of 1550 nm can penetrate thin fog and light smoke (with lower attenuation compared to 905 nm), while microwave radars have stronger penetration through rain and snow but sacrifice accuracy.
Multi-Sensor Integration
Although LiDAR excels in long-range detection and 3D object recognition, it has limitations in close-range sensing and texture identification . No single sensor can fully meet all perception requirements, which is why LiDAR is often combined with other sensors (such as cameras, radar, and IMU) to achieve more comprehensive environmental perception and higher operational reliability through sensor fusion technology.
Cameras: LiDAR provides accurate 3D point cloud data via laser ranging, supporting depth perception and distance measurement to objects. Cameras deliver high-resolution color images that enable object recognition and classification. For example: LiDAR can detect the shape and position of an object, while a camera can determine whether it is a vehicle, pedestrian, or another type of obstacle.
Radar: Provides speed and distance information under various weather conditions. LiDAR delivers high-precision (millimeter-level) distance measurements within short to medium ranges (10–200 meters), but its performance can be affected by rain or fog. Radar performs well at longer distances (50–250 meters), is unaffected by weather conditions, and can penetrate fog or dust.
Inertial Measurement Unit (IMU): Measures the robot's acceleration and angular velocity, providing motion and orientation information. It supports short-term localization in GPS-denied environments.
Ultrasonic Radar Sensors: Used for close-range object detection, such as parking assistance or proximity operations.
Industry Applications
LiDAR is known for its high-precision and all-weather environmental perception capabilities, has been widely adopted across multiple industries. Its core advantage lies in the ability to generate high-resolution 3D environmental models, meeting the demands of complex lighting conditions and dynamic scenes.
Logistics and Warehousing
LiDAR helps freight robots build 3D maps of warehouses, enabling efficient transportation and inventory management.
Example: Amazon’s Kiva robots use similar technology for warehouse automation and item retrieval.
Industrial Automation
Supports robotic precision operations on assembly lines, such as part positioning or inspection in confined spaces.
Example: In General Electric factories, LiDAR assists robotic arms in performing accurate welding tasks.
Outdoor Agriculture and Forestry
Enables agricultural robots to navigate fields and perform tasks like precision seeding, weeding, and crop monitoring.
Example: Agricultural LiDAR helps robots assess crop health and plan optimal paths for treatment or harvesting.
Commercial Facilities
(Malls, Hospitals, Hotels): Helps robot chassis detect people and furniture, ensuring safe and reliable service delivery.
Example: Service robots use LiDAR to identify and guide customers.
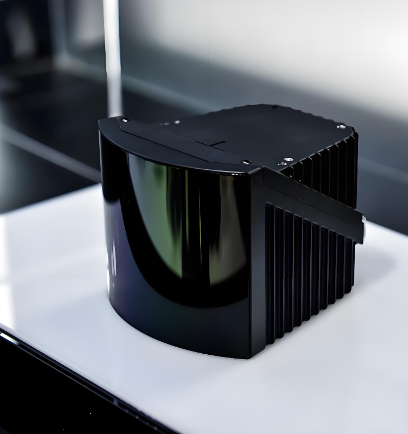
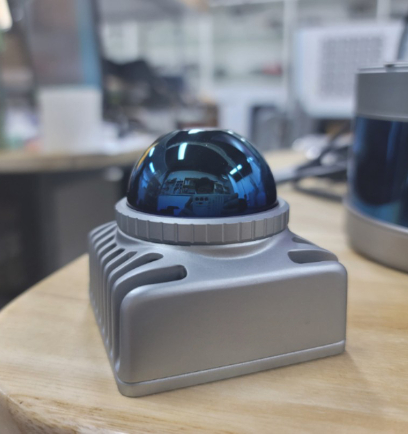
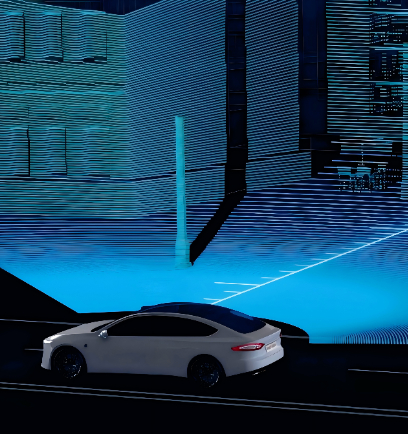


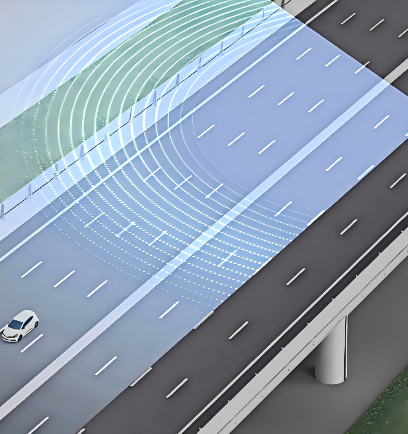

Product Classification
Accelerating the Robot Dream
Empowering robot innovation, providing full-cycle development services, reducing costs, and accelerating the commercialization process.
Contact Us +